Your cart is currently empty!
Best RSI setting for swing trading
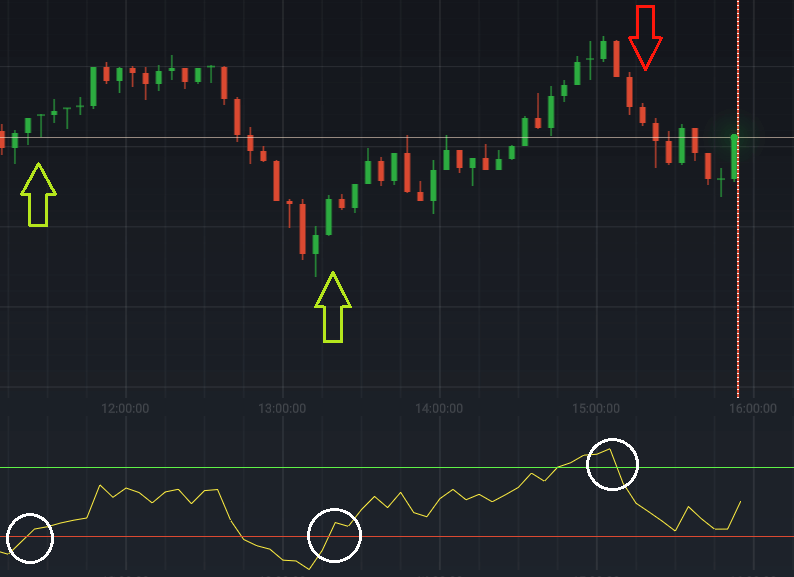
If you want to get good at trading stocks, using tools like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can be very helpful. The RSI is like a special score that tells you if a stock is likely to go up or down. In swing trading, where you buy and sell stocks over a few days or weeks to make money, the RSI can help you decide when to buy or sell.
What is RSI?
RSI stands for Relative Strength Index. It’s a tool that traders use to see how strong a stock is right now. It gives a number between 0 and 100. A number above 70 usually means the stock is “overbought,” which means it might go down soon. A number below 30 means the stock is “oversold,” which means it might go up soon.
Choosing the Right RSI Setting
The standard setting for RSI is 14 periods. This means it looks at the last 14 time periods (like days or hours) to calculate the number.
- Shorter Periods (like 9 or 12): These can give you more signals (like “buy” or “sell”), but they might not always be accurate.
- Longer Periods (like 21 or 28): These can filter out bad signals but might miss some good chances to trade.
You can try different settings to see which one works best for you.
Following the Trend
A trend is like a direction the stock price is moving in, either going up or down.
- Going Up: If the stock is generally going up, you might want to buy when the RSI shows the stock is oversold (below 30).
- Going Down: If the stock is going down, you might want to sell when the RSI shows the stock is overbought (above 70).
Understanding Overbought and Oversold
Remember, the numbers 70 and 30 aren’t hard rules.
- In a strong uptrend (when the stock is going up a lot), the RSI might stay above 70 for a while.
- In a strong downtrend (when the stock is going down a lot), the RSI might stay below 30 for a while.
Looking Beyond the Numbers
While the RSI is a good tool, it’s best to use it with other information.
- Chart Patterns: Look for shapes like a “head and shoulders” or “double top/bottom” to confirm what RSI is telling you.
- Support and Resistance: These are levels where the price has a hard time moving below (support) or above (resistance).
Being Careful When Trading
To be a successful trader, you need a plan.
- Plan Your Trades: Know when you want to buy and sell before you make a trade.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: This is like setting a point where you sell automatically to prevent losing too much money.
- Position Sizing: Decide how much money to trade on each trade to manage risk.
Keep Learning and Adapting
The stock market changes all the time, so keep learning and adapting your strategies.
- Review Your Trades: Look back at your trades to see what worked and what didn’t.
- Stay Updated: Keep up with the latest news and trends in the market.
- Improve Your Strategies: Keep trying new things and adjusting your strategies.
Understanding RSI Divergences
Divergences happen when the price and the RSI are not moving in the same direction.
- Regular Divergence: When the price makes a new high or low but the RSI doesn’t, it might mean a trend is going to change.
- Hidden Divergence: When the price makes a lower low but the RSI makes a higher low (or the opposite), it can mean the current trend might continue.
Combining RSI with Other Tools
You can use the RSI with other tools to get a better picture.
- Moving Averages: When the RSI is oversold and the stock is above a key moving average, it could be a good time to buy.
- Bollinger Bands: These bands show volatility. When the RSI is oversold and the price is near the lower band, it might be a good time to buy.
- Volume: If there’s a lot of trading happening (high volume) along with an RSI signal, it makes the signal stronger.
Building a Trading System with RSI
Here’s a simple trading plan using RSI:
- Find a Trend: Use moving averages to see if the stock is going up or down.
- Look for RSI Signals: Wait for the RSI to show oversold (below 30) or overbought (above 70) conditions.
- Confirm with Price Action: Check if there are other signs like patterns or support/resistance levels.
- Set Your Stop-Loss: Protect yourself by setting a stop-loss order.
- Decide on Profit Targets: Set a goal for how much profit you want to make.
Example: Using RSI in Real Life
Imagine you are looking at a technology stock called “TechCorp”:
- Identify the Trend: TechCorp’s stock has been going up for a few months.
- Spot a Divergence: The stock price makes a new high, but the RSI doesn’t, which shows a bearish divergence.
- Confirm with Price Action: At the same time, a bearish candlestick pattern shows up, suggesting the price might go down.
In this case, you might want to sell TechCorp or reduce your holdings, expecting a drop in price.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Here are some mistakes to avoid when using RSI:
- Relying Too Much on RSI: Don’t make decisions based only on RSI. Always use other tools and information.
- Ignoring the Market Context: RSI works best in trending markets, not in choppy or sideways markets.
- Chasing Overbought/Oversold Levels: Don’t buy just because RSI says oversold or sell just because it says overbought. Check other factors too.
- Forgetting Risk Management: Always use stop-loss orders to protect your money.
- Lack of Discipline: Stick to your plan and don’t let emotions guide your trades.
Tips for Using RSI Successfully
- Backtesting: Test your strategies using old data to see if they work.
- Stay Flexible: Be ready to change your plan as the market changes.
- Keep Learning: Learn more about technical analysis and stay updated on market trends.
- Diversify: Don’t put all your money in one stock or strategy. Spread your investments out.
By following these simple steps and understanding how to use RSI for swing trading, you can become a better swing trader and increase your chances of making money in the stock market.
FinQuiz
Which company developed Material Design?

Mr. Rajeev Prakash
Rajeev is a well-known astrologer based in central India who has a deep understanding of both personal and mundane astrology. His team has been closely monitoring the movements of various global financial markets, including equities, precious metals, currency pairs, yields, and treasury bonds.

